Prevent and manage diabetes with lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Learn strategies for reducing risk and living well with diabetes.
Diabetes Prevention and Management: A Comprehensive Guide
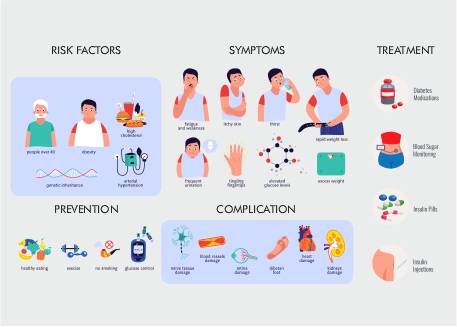
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing significant health complications if not managed properly. The good news is that type 2 diabetes, which accounts for more than 95% of diabetes cases, is largely preventable through lifestyle changes and early intervention. This article will delve into the strategies for preventing diabetes and managing its symptoms effectively.

Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition where the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is crucial for regulating blood glucose levels. When diabetes is uncontrolled, it can lead to serious health issues such as blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, and lower limb amputations.
Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: This form of diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. It typically develops in childhood or adolescence and requires insulin therapy for survival.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This is the most common form of diabetes and occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin. It is often linked to obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type of diabetes develops during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester. It typically goes away after pregnancy but increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing diabetes involves making conscious lifestyle choices that promote overall health and reduce the risk factors associated with type 2 diabetes.
1. Maintain Healthy Weight
Being overweight or obese significantly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Losing weight can help reduce this risk. Even a modest weight loss of 7-10% of your current weight can cut your chances of developing diabetes in half.
2. Stay Physically Active
Regular physical activity is crucial for preventing diabetes. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week. Activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling are excellent options. Even simple changes like taking the stairs instead of the elevator can make a difference.
3. Eat a Balanced Diet
A healthy diet plays a vital role in prevention of diabetes. Focus on consumption:
- Fiber-rich foods: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet. Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes satiety.
- Healthy fats: Nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil are good sources of healthy fats.
- Lean proteins: Choose lean meats, fish, and plant-based proteins like beans and lentils.
- Limit refined carbohydrates and sugars: Avoid foods high in sugar and refined carbs, such as white bread and sugary drinks.

4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps control blood sugar levels and reduces the intake of sugary beverages.
5. Quit Smoking
Smoking can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Quitting smoking can help reduce this risk over time.
Management Strategies
For those already diagnosed with diabetes, effective management is key to preventing complications.
1. Medication and Insulin Therapy
Depending on the type and severity of diabetes, medication or insulin therapy may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels. Common medications include metformin, sulfonylureas, and SGLT-2 inhibitors.
2. Regular Monitoring
Regular blood glucose monitoring and health check-ups are crucial for managing diabetes effectively. This helps in identifying any complications early and adjusting treatment plans accordingly.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for managing diabetes. This includes continuing to follow the prevention strategies mentioned above, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Stress Management
Stress can impact blood sugar levels and overall health. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress effectively.

FAQs
- What are the main risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
- Being overweight or obese, physical inactivity, an unhealthy diet, and genetics are major risk factors.
- How can I prevent type 2 diabetes?
- Maintain a healthy weight, stay physically active, eat a balanced diet, avoid smoking, and limit alcohol consumption.
- What are the common complications of diabetes?
- Diabetes can lead to blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke, and lower limb amputation if not managed properly.
- How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
- The frequency depends on your type of diabetes and treatment plan. Generally, regular monitoring is advised, especially if you are on insulin therapy.
- Can diabetes be cured?
- While there is no cure for diabetes, it can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes and medical treatment, reducing the risk of complications.
Additional Tips for Diabetes Management
1. Foot Care
People with diabetes are at risk of foot complications due to nerve damage and poor circulation. Regularly inspect your feet for any signs of injury or infection and consult a healthcare provider if you notice anything unusual.
2. Eye Care
Diabetes can lead to vision problems, including diabetic retinopathy. Regular eye exams are crucial for early detection and treatment.
3. Dental Care
Diabetes increases the risk of gum disease and other dental issues. Practice good oral hygiene and visit your dentist regularly.
4. Travel Precautions
If you have diabetes, it’s important to take extra precautions when traveling, such as packing a diabetes emergency kit and informing your airline or travel companions about your condition.
5. Emotional Support
Living with diabetes can be challenging emotionally. Consider joining a support group or seeking counseling to manage stress and stay motivated.
Conclusion
Diabetes prevention and management require a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and, when necessary, medical treatment. By adopting healthy habits and being proactive about your health, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes and manage its symptoms effectively if you are already diagnosed